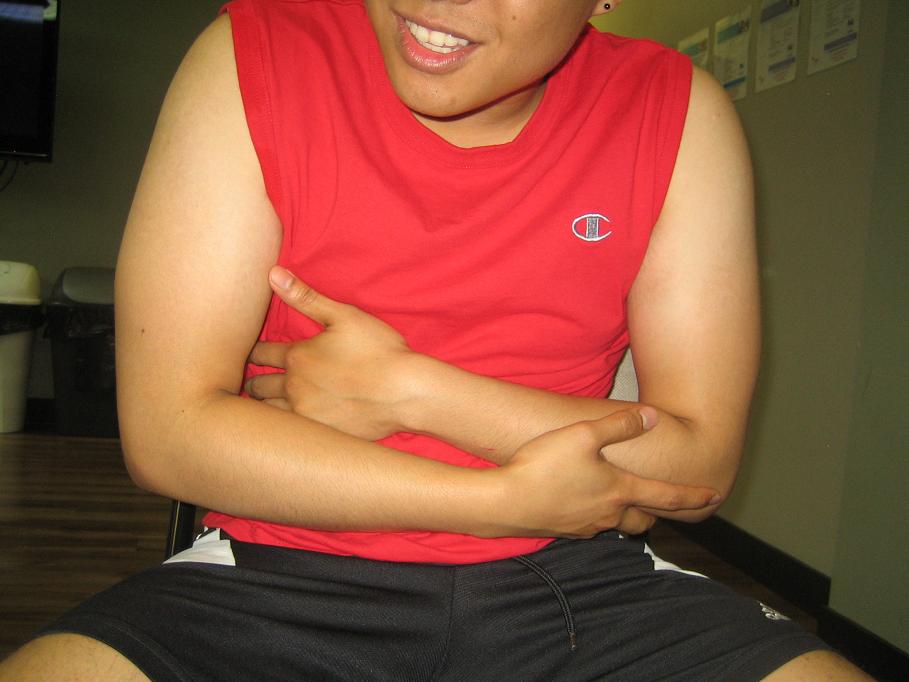
An abdominal strain is a tear or rupture of abdominal muscles usually at the point where it is connected to the pelvis. It causes pain, inflammation and weakness due using improper techniques during workouts or lifting of heavy objects. Any sports that require fast or sudden changes in direction such as weight lifters, gymnasts, throwers, and rowers are susceptible to abdominal muscle strain.
Grades
- Grade 1 strain happens when few fibers of muscles are torn
- For a grade 2 strain, it happens when the tears are more severe.
- Grade 3 strain happens when there is a complete rupture of the muscle
Causes
- Improper warm up and cooling down
- Poor posture
- Poor core stability and strength
- Trauma to the stomach
- A sudden explosive movement
- Overuse of the abdominal muscles
- Overstretching
Symptoms
- At first, there is tenderness of the area
- Cramping of the muscles
- Tightness of the affected area
- Swelling
- Pain when the muscles of the stomach are contracted
- Lastly, sudden pain which indicate a rupture
Treatment for an abdominal strain
- Apply ice pack on the affected area for at least 15 minutes, 3 times every day to lessen the inflammation and relief from the pain. Wrap ice using a towel before placing to the area to prevent ice burn and worsen the condition. Another alternative is massage the affected area using an ice in a circular motion for at least 15 minutes, 3 times every for fast healing of the condition.
- Eat foods rich in protein that include fish, lean meats, milk, poultry, eggs and cheese which is needed for repair of muscles.
- After 24 hours apply heat in the area in the form of heat lamps, heating pads or hot compress. Heat relaxes the muscles, lessen the inflammation and for fast healing of the condition. Stop using heat if it causes discomforts and result to irritation on the skin.
- Wrap the abdomen using a bandage and apply a slight compression. Avoid wrapping it too tight to prevent problems with circulation.
- Keep the affected area in level with the heart to increase flow of blood in the area.
- When the pain and the inflammation begin to lessen, perform some gentle stretching to repair function of the muscle and prevent scarring of the tissue.
- Avoid lifting heavy weights or exercises to prevent further injury such as development of intestinal herniation and worsen the condition.
- Take plenty of rest which is needed for fast healing of the condition.
- Provide the given anti-inflammatory medication to lessen the swelling and the pain.
- Consult a physical therapist for some rehabilitation exercises for recovery and strengthen the muscles.
Tips
- Avoid overexerting the body while performing exercises.
- Perform the proper way of lifting heavy objects
- Perform exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles
- Get proper training for exercises and sports
Disclaimer / More Information
The material posted on this page on an abdominal strain is for learning purposes only. Learn to properly manage the injury by taking a first aid and CPR class with one of our training providers.
FACT CHECK
https://www.summitmedicalgroup.com/library/adult_health/sma_abdominal_muscle_strain/
https://www.healthline.com/health/abdominal-strain
https://www.sportsmd.com/sports-injuries/abdominal-injuries/abdominal-strain/