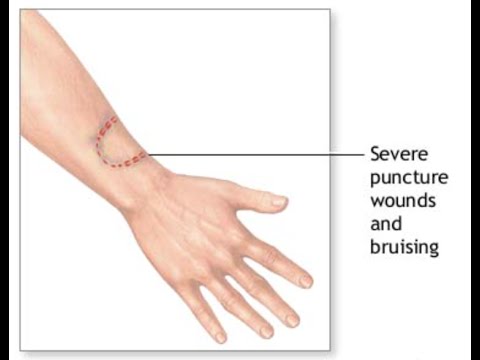
A human bite wound happens because of incidental or purposeful injury and high risk for infection. Most injuries caused by a human bite involve the hands and has high risk of infection than those in other areas of the body. The bites can transmit hepatitis C, hepatitis B, herpes simplex virus, tuberculosis, syphilis, actinomycosis and tetanus.
Causes
- Domestic violence
- Child abuse
- Aggressive behavior due to drinking alcohol
- Occupational injuries to dental personnel
- Aggressive playing of children
- Accidental sports injuries
Severe pain usually begins 1-2 days after the bite but happens later with deeper infections. - Seizure-related lacerations on the tongue
- Self-inflicted wounds among individuals who are emotional disturbed or mentally handicapped that includes self-mutilation through biting
Symptoms of a human bite
- A break in the skin
- Severe pain usually begins 1-2 days after the bite but happens later with deeper infections.
- Changes in the skin coloration. Bruising and redness that eventually becomes worse after a few hours. Severe redness is a symptom of an infection.
- Swelling
- Fever
- Pus drainage
- Red streaks that spread toward the center of the body from the infected wound.
- Swollen glands
Treatment
- Check for current vaccinations and other medical conditions such as hepatitis. Hepatitis and tetanus can develop when a human bite develops an infection.
- Stop the bleeding by applying pressure. Apply pressure on the affected area using a clean and dry cloth or bandage. Lie down on a bed if bleeding is severe to prevent losing body heat and preventing shock. If the bandage is soaked with blood, do not remove it. Place another cloth over it until the bleeding stops. If fragments of a tooth are still in the wound, avoid applying too much pressure and do not attempt to remove the object.
- Once the bleeding stops, wash the wound using soap and water to remove any bacteria and lessen the risk of infection. Another alternative is washing the wound using povidone iodine which has antibacterial properties that can be applied directly on the wound or with a bandage.
- Apply an ice pack on the bite site for at least 15 minutes to lessen the pain and swelling.
- Apply the prescribed antibiotic ointment such as neomycin on the bite site to prevent infection, lessen pain and swelling and promote fast healing of the condition.
- Cover the wound using a clean bandage once the bleeding is controlled and disinfected to minimize exposure of the area to bacteria and prevent infection.
More Information
The details posted on this page on human bites is for learning purposes only. To learn to provide proper wound care for a human bite, enroll in a first aid course with one of our training providers.
FACT CHECK
https://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-human-bites/basics/art-20056633