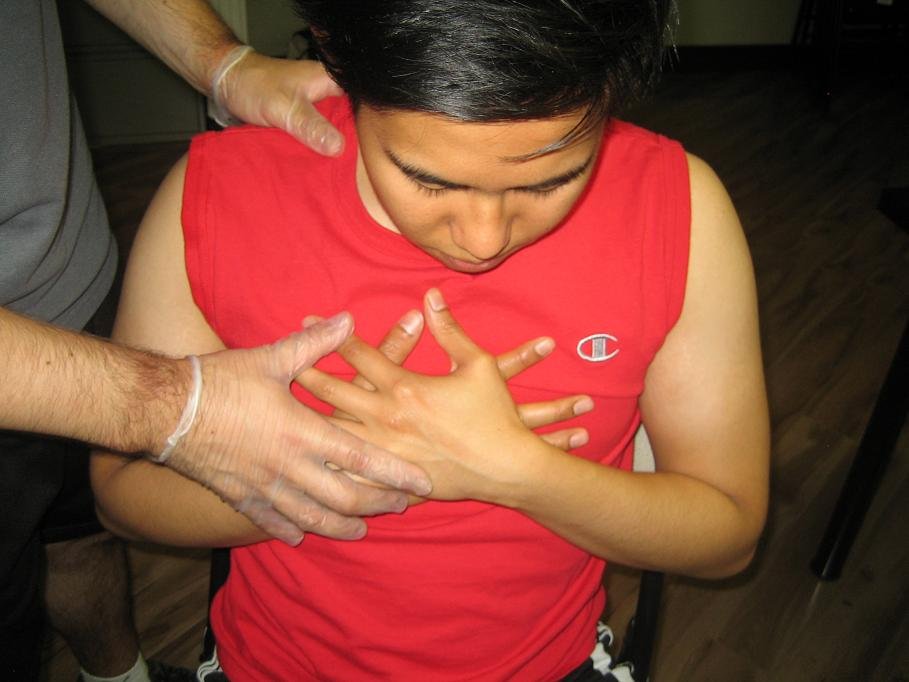
Costochondritis arises when the cartilage found between the rib and breastbone or sternum becomes swollen and inflamed. It is a common cause of chest pain in adolescents and children.
What are the causes?
- Frequent minor damage to the chest wall
- Respiratory infections due to viruses
- Relapsing polychondritis
- Fibromyalgia
- Reactive arthritis
- Bacterial infections from using recreational IV drugs or surgery on the upper chest
- Certain forms of arthritis such as anklylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis and breastbone pain
Symptoms of costochondritis
- Severe chest pain when performing exercises, minor injury or infections of the upper respiratory system.
- Reproducible tenderness when joints of the ribs or costochondrial joints are pressed
- Intense chest pain can be felt on the front chest wall. The pain will spread from the chest area to the back or abdomen and result to pain in the back or pain in the belly.
- Pain can be felt on the fourth, fifth and sixth ribs, and becomes severe especially with movement of the trunk or when breathing deeply.
- Redness, swelling or pus discharge and inflammation due to infections after a surgery
Treatment
- Get plenty of rest especially the affected area for fast healing of the condition. Avoid performing activities that requires sharp moves, high stress on the chest muscles and a high risk of blows to the chest includes tennis, golf, baseball, karate and basketball.
- A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as ibuprofen and naproxen can be used to reduce the pain and the inflammation.
- Apply heat to the affected area for proper flow of blood and lessen the tension in the muscles. Use hot water bottle or a heating blanket. Avoid heat directly on the skin to prevent burns and worsen the condition. Wrap it using a towel or a piece of cloth before applying to the area for at least 10-15 minutes.
- Apply ice pack on the affected area to lessen the swelling and soothe the inflammation. place ice cubes in a plastic bag and wrapped in a towel or a clean cloth before placing to the area for at least 15-20 minutes at a time 3-4 times every day. Avoid ice directly on the skin to prevent further irritation and worsen the condition. If ice is not available, a bag of frozen vegetable such as peas or corn is good for the condition.
- Perform gentle stretching the tight chest muscles around the joint with the help of the physical therapist. Begin with gentle stretching of the chest muscles with slow deep breaths. If the exercises cause pain, stop immediately to prevent further injury.
- Improve posture to lessen straining of the chest. Avoid sitting or standing with a hunched posture to prevent symptoms of costochondritis and lessen the pain. Sit, stand and walk with a book balanced on the head. Open the chest and let the shoulders roll back.
FACT CHECK
https://www.healthline.com/health/costochondritis
https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/costochondritis#1
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/costochondritis/symptoms-causes/syc-20371175