A head injury is any form of trauma to the skull, scalp or brain which can be a minor crash on the skull or a significant brain injury.
Generally, a head injury can be categorized as closed or open or penetrating. A closed injury is caused by a hard blow to the head from an object while an open or penetrating head injury involves a break in skull. In addition, this injury usually happens when moving at high speed such as in a vehicular accident and a gunshot wound.
Causes of a head injury
- Falls
- Physical assault
- Traffic accidents
Symptoms
- At first, bleeding in the tissue and the layers surrounding the brain such as the subarachnoid hemorrhage, epidural hematoma and subdural hematoma.
- Symptoms can develop right away or slowly for several hours or days
- Even if the skull is not fractured, the brain inside the skull can be damaged and bruised. In addition, in some cases, there is no damage on the head but there is bleeding or swelling inside the skull.
- Lastly, the spinal cord can be affected by any serious trauma
Treatment
- Check the airway, breathing and circulation of the affected person. If needed, start rescue breathing and CPR.
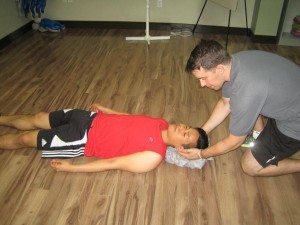
- If the breathing and heart rate is normal but the person is unconscious, stabilize the head and neck by holding the head of the person and keep it aligned with the spine and prevent the head from any movement until help arrives.
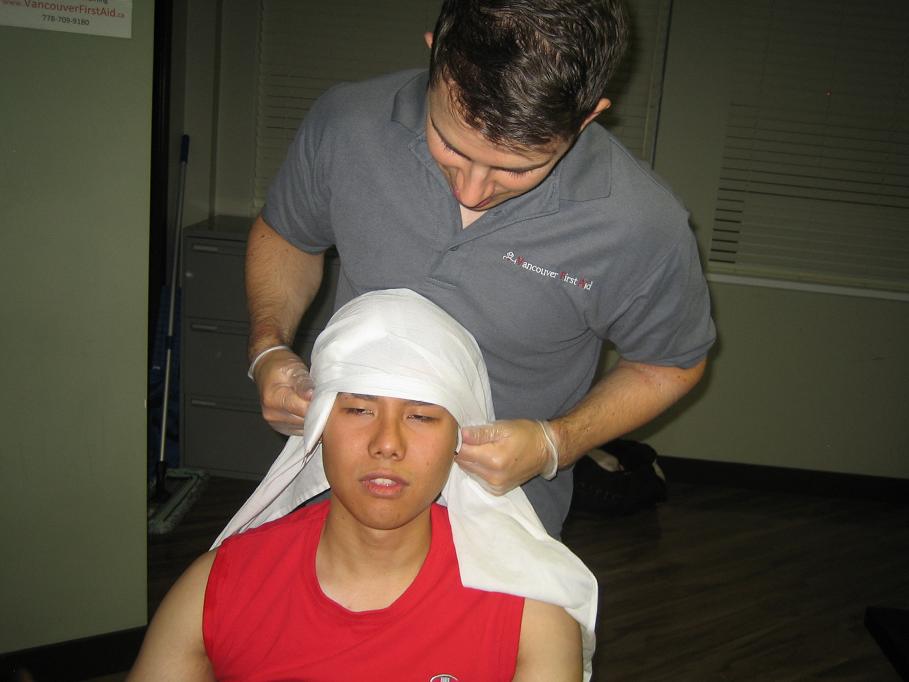
- Stop any bleeding by using a clean cloth and press it firmly on the wound. Generally, if the injury is very severe, avoid moving the head. If blood soaks the cloth, place another cloth over the first one.
- If a fracture is likely, avoid applying direct pressure to the area and removing any debris found in the wound. Furthermore, cover the wound using a sterile guaze dressing.
- Roll the head, neck and body together if the affected person is vomiting to prevent choking. In addition, children are prone to vomit after a head injury
- Apply an ice pack to the swollen areas. Avoid applying ice directly on the scalp. Furthermore, wrap the ice pack in a small towel before applying to the area.
More Information
The details posted on this page on head injuries is for learning purposes only. To learn to recognize and manage head injuries, enroll in a first aid course with one of our training providers.
Tips
- Do not wash a wound on the head that is deep and bleeding profusely.
- Avoid removing objects that are sticking out of the wound.
- Do not remove the helmet if a severe head injury is likely.
- Avoid picking up a child with a head injury
FACT CHECK
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000028.htm
https://www.healthline.com/health/head-injury
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/traumatic-brain-injury/symptoms-causes/syc-20378557